5 things to know as Dr. Oz gets one step closer to leading Medicare and Medicaid
NPR Health
MARCH 25, 2025
The former TV doctor made it through a tight vote in the Senate Finance committee with only Republican support.

NPR Health
MARCH 25, 2025
The former TV doctor made it through a tight vote in the Senate Finance committee with only Republican support.
The Hindu
MARCH 25, 2025
Multiple vaccine-related petitions that have been filed before courts reflect growing concerns about how vaccines are approved and administered in India
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

NPR Health
MARCH 25, 2025
A tour of a grow facility in Maryland reveals the wide variety of scents from different cannabis strains.

The Hindu
MARCH 25, 2025
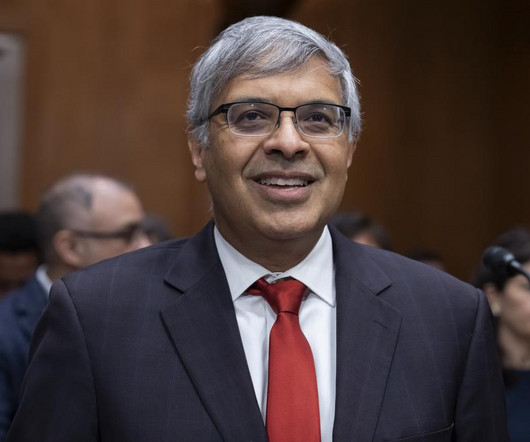
Indian-American scientist Jay Bhattacharya confirmed as NIH Director by U.S. Senate, focused on improving health with gold-standard science.

NPR Health
MARCH 25, 2025
The government in Nigeria is warning about the health risks of skin lightening, where potent chemicals can thin and damage skin. It's a booming business in that country and others.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Whether it's an early morning jog, or a touch of Tai Chi, groundbreaking research shows that any form of exercise can significantly boost brain function and memory across children, adults, and older adults.
Public Health Engage brings together the best content for public health professionals from the widest variety of industry thought leaders.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Early animal studies show that a single vaccine could protect the recipient from different variants of the coronaviruses that cause COVID-19, the flu and the common cold. In addition to creating antibodies that target a specific region of the spike protein that doesn't mutate, the vaccine removes the sugar coat from the virus that allows it to hide in the body.
News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Ochsner Health Medical Director for Cardiac Rehabilitation and Preventive Cardiology, Carl J. "Chip" Lavie, Jr., MD, recently co-authored a groundbreaking research study featured in the prestigious Mayo Clinic Proceedings highlighting the comparative efficacy of lipid-lowering therapies for reducing cardiovascular risks and led by Maciej Banach, MD,PhD from Poland and leader of the International Lipid Expert Panel ( ILEP).

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Tiny fragments of plastic have become ubiquitous in our environment and our bodies. Higher exposure to these microplastics, which can be inadvertently consumed or inhaled, is associated with a heightened prevalence of chronic noncommunicable diseases, according to new research.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
A 30-year study of over 100,000 U.S. adults found that consistent adherence to healthy dietary patterns, especially the AHEI, was strongly linked to successful aging. Diets rich in plant-based foods and healthy fats, with some low-fat animal products, improved physical, mental, and cognitive health.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
By watching the ebb and flow of the brain's chemical signals, researchers are beginning to disentangle the molecular mechanisms underlying the intrinsic motivation to learn. In a new study of zebra finches, researchers show that a hit a dopamine tells baby birds when their song practice is paying off. The findings suggest that dopamine acts like an internal 'compass' to steer their learning when external incentives are absent.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Tiny fragments of plastic have become ubiquitous in our environment and our bodies. Higher exposure to these microplastics, which can be inadvertently consumed or inhaled, is associated with a heightened prevalence of chronic noncommunicable diseases, according to new research being presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Life needs sufficient phosphorus. However, the element is scarce, not only today but also at the time of the origin of life. So where was there sufficient phosphorus four billion years ago for life to emerge? A team of origin-of-life researchers has an answer.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
The most comprehensive model of the brains metabolism, incorporating more than 16,800 biochemical interactions, has identified key targets to reverse the age-related decline in brain function.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
This a robot can walk, without electronics, and only with the addition of a cartridge of compressed gas, right off the 3D-printer. It can also be printed in one go, from one material.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
New research from Auckland University of Technology reveals that eight native New Zealand honeys, beyond mnuka, possess unique antioxidant, antibacterial, and bioactive properties. Thyme and beech honeydew stood out for their vitamin C and polyphenol content.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
The condition of the grass on a golf course can drastically skew the chances of a winning putt regardless of a player's skill. Now, a coating that soaks up water molecules could slow the roll of a golf ball on a lightning-fast, dry course and speed it up on a sluggish, wet course without interfering with the ball when it's airborne.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
A new review was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 13, 2025, titled "Signaling pathway dysregulation in breast cancer.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Mothers experience major metabolic adaptations during pregnancy and lactation to support the development and growth of the new life. Although many metabolic changes have been studied, body temperature regulation and environmental temperature preference during and after pregnancy remain poorly understood. Researchers show that postpartum female mice develop new environmental temperature preferences and reveal brain changes mediating these changes.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Exposure to antibiotics during a key developmental window in infancy can stunt the growth of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and may boost risk of diabetes later in life, new research in mice suggests.
The Hindu
MARCH 25, 2025
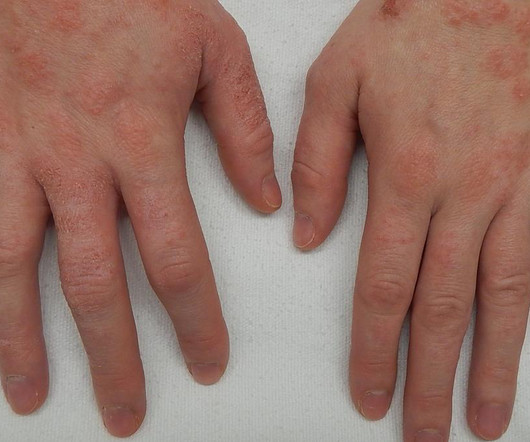
There are many different types of eczema, each requiring the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment; stress reduction and a well-balanced lifestyle can help improve immunity
News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Zika virus and dengue virus are very close relatives. Both are mosquito-borne flaviviruses, and both specialize in infecting a host's dendritic cells.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
From virtual reality to rehabilitation and communication, haptic technology has revolutionized the way humans interact with the digital world. While early haptic devices focused on single-sensory cues like vibration-based notifications, modern advancements have paved the way for multisensory haptic devices that integrate various forms of touch-based feedback, including vibration, skin stretch, pressure and temperature.
News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Mothers experience major metabolic adaptations during pregnancy and lactation to support the development and growth of the new life.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Deep below the Earth's surface, rock and mineral formations lay hidden with a secret brilliance. Under a black light, the chemicals fossilized within shine in brilliant hues of pink, blue and green. Scientists are using these fluorescent features to understand how the caves formed and the conditions for supporting life in extreme, and even extraterrestrial, environments.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Closed Loop Medicine Ltd., a leader in AI-enabled precision medicines, today announced the expansion of its US patent portfolio. Strengthening its cardiometabolic treatment portfolio, the Company now has patents covering advancements in GLP-1 therapies for obesity and diabetes, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) for cardiovascular health.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
To get around the constraints of quantum physics, researchers have built a new acoustic system to study the way the minuscule atoms of condensed matter talk together. They hope to one day build an acoustic version of a quantum computer.

News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Psychologists find most TikTok videos about ADHD to be misleading, often overgeneralizing normal behaviors as symptoms. These videos shape young adults perceptions and contribute to rising self-diagnosis trends.

Mercola
MARCH 25, 2025
Photobiomodulation (PBM) therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), is a noninvasive therapeutic modality that utilizes light within specific wavelengths to stimulate beneficial biological processes in living tissues. 1 This article explores the benefits and penetration depths of three distinct wavelengths: 660 nanometers (nm), 850 nm and 1,050 nm.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
MARCH 25, 2025
Research has shown that a biological brain mechanism called the 'kynurenine pathway' is imbalanced in adolescents with depression, and this imbalance is more pronounced in teenage girls than boys.
News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
Sugar coatings aren't only for candies; they also help viruses, like the ones that cause COVID-19, hide from their hosts' immune system.

The New Social Worker
MARCH 25, 2025
We can create enduring action in our workplaces through enhanced compassion for each other. Indeed, if we are to persist, in political times that require social workers now more than ever, we must.
News Medical Health Sciences
MARCH 25, 2025
A Japanese research team has discovered a novel global cooperative phenomena of cell interactions in cervical cancer cells. Their findings suggest that the cells are metabolically connected in a functional network.

Mercola
MARCH 25, 2025
When was the last time you paid attention to your nails aside from keeping them trimmed? While looking at your nails from time to time is normal, they actually provide a window to your current health. In a HuffPost article, aging and genetics expert David Sinclair, Ph.D., explains what your nail growth can tell you about your aging process, and the basis for his hypothesis, which was published way back in 1979. 1 Nail Growth Is a Hidden Marker of Aging The 1979 study referenced by Sinclair, publ
Let's personalize your content