Upheaval and firings at CDC raise fears about disease outbreak response
NPR Health
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Staff and observers worry that the agency may not be prepared for emerging threats including bird flu and insect-borne diseases.
NPR Health
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Staff and observers worry that the agency may not be prepared for emerging threats including bird flu and insect-borne diseases.

NC Health News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
By Taylor Knopf Last month, the state health department announced $13 million in funding to open four new community mental health crisis facilities in Lenoir, New Hanover and Pitt counties by the end of the year. This is one of a flurry of new mental health initiative announcements from the state Department of Health and Human Services that have come as a result of a $835 million investment for behavioral health needs included in the 2023 state budget.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Making enemies isn't random. Traits like emotional instability, aggression, and disruptive behavior early in life can lead to antagonistic relationships. Research on students aged 9-14 found that negative behaviors, such as lack of empathy, increase the likelihood of mutual antagonisms, a pattern seen across genders and school levels. Emotionally struggling students were 35% more likely to develop enemies, showing that how we manage emotions and interact with others early on can have lasting soc

Association of Health Care Journalists
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A recent study clearly defined 12 harmful elements used when reporting on gun violence; rating them as mild, moderate, or severe across individual, community and societal levels. News stories that include graphic content, use episodic framing of individual incidents with little or no context, leave out potential solutions, and rely only or mostly on law enforcement sources instead of impacted community members can cause harm on all three levels, the study determined.

NPR Health
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
The case counts seem to be dropping. But health officials say that's because violence in the Democratic Republic of Congo makes it difficult to get good data. And now U.S. assistance is being disrupted.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Keeping work surfaces clean during meat processing is a challenge, and now researchers deliver key insights into a solution that could change the current practice altogether: Instead of working to prevent bacteria buildup, they created surfaces that stop bacteria from attaching in the first place. Using lasers to etch and alter the surface of the metal, the team was able to create micro- or nanoscale textures that make it difficult for microbial cells to attach to the surface.
Public Health Engage brings together the best content for public health professionals from the widest variety of industry thought leaders.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A bone marrow transplant process is safe and curative for adults with sickle cell disease, according to results of a trial completed at about 20 cancer centers.

News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Life expectancy gains in Europe slowed after 2011, with the COVID-19 pandemic further accelerating declineswhile some countries maintained progress through sustained public health policies.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Hormones may be leveraged to treat and prevent signs of aging such as wrinkles and hair graying, according to a new study.
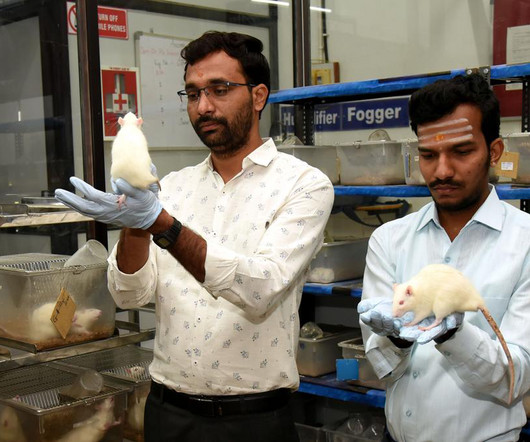

The Hindu
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
The scientists told mediapersons in Kalaburagi that the chemical compounds Isobutyal Parabal found in some cosmetics and Phenyl Mercuric Acetate found in herbicides are one of the major reasons for endocrine disruptions and hormonal imbalances in the two generation studies on the sexual behaviour of rats and mice conducted in the Animal House of the Sharnbasva University.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
The Beatles said it best: Love is all you need. And according to new research, the same may be true in the animal kingdom. Well, at least for mosquitofish -- a matchstick-sized fish endemic to Central America and now found globally. According to the scientists, male mosquitofish possess impressive problem-solving skills and can successfully navigate mazes and other tests.

News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Researchers explore how artificial intelligence is transforming infectious disease modeling

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A new study shows a water-rich mineral could explain the planet's color -- and hint at its wetter, more habitable past.

The Hindu
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
There is currently no integrated method to collect data from hospitals, police, and educational institutions.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
New observations of 2024 YR4 conducted with the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT) and facilities around the world have all but ruled out an impact of the asteroid with our planet. The asteroid has been closely monitored in the past couple of months as its odds of impacting Earth in 2032 rose to around 3%, the highest impact probability ever reached for a sizable asteroid.

News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Scientists have identified a novel influenza A virus (H18N12) in fishing bats in the Colombian Caribbean, revealing genetic reassortment events that impact viral adaptability and host transmission.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Our organs age at different rates, and a blood test determining how much they've each aged could predict the risk of conditions like lung cancer and heart disease decades later, finds a new study.

News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Higher coffee consumption is causally linked to delayed onset of Parkinsons disease but does not affect disease risk or progression, according to a Mendelian randomization study.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A new study suggests that Neanderthals experienced a dramatic loss of genetic variation during the course of their evolution, foreshadowing their eventual extinction. Examination of semicircular canals of ear shows Neanderthals experienced 'bottleneck' event where physical and genetic variation was lost.
News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Three months after her breakthrough surgery at NYU Langone Health, Towana Looney, the longest-living recipient of a genetically engineered pig kidney, is headed back home to Alabama.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
With ideal conditions and strategic pacing and drafting, Kenyan Faith Kipyegon is on the brink of hitting the fabled track and field milestone, a new study suggests. The authors are now calling for a staged 'Breaking 4' event to help her do it.
News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A newly published study in Genes & Diseases highlights the crucial role of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway in the progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN) and explores its potential as a therapeutic target.
The Hindu
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
The field of cardiac interventional care is advancing rapidly, paving the way for more precise, less invasive treatments that are making it possible to treat heart disease more effectively with fewer complications

News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Vitamin D supplementation shows no significant effect on acute respiratory infections overall, but children and daily low doses may offer protective benefits.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Researchers have developed a battery that can convert nuclear energy into electricity via light emission, a study suggests.

Berkeley Public Health
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Now celebrating its 50th anniversary, the program remains devoted to its mission: promoting safe, healthy, and just workplaces.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Astronomers have discovered that the Solar System traversed the Orion star-forming complex, a component of the Radcliffe Wave galactic structure, approximately 14 million years ago. This journey through a dense region of space could have compressed the heliosphere, the protective bubble surrounding our solar system, and increased the influx of interstellar dust, potentially influencing Earth's climate and leaving traces in geological records.
News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Early diagnosis of lung cancer is a critical priority in clinical practice. It may help reduce the rate of lung-cancer-related mortality, extend disease-free survival, and allow patients to live without ongoing medical interventions and complications.

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
On Wednesday 26 February, a thermal imaging camera blasted off to the Moon as part of NASA's Lunar Trailblazer mission. This aims to map sources of water on the Moon to shed light on the lunar water cycle and to guide future robotic and human missions.

The Hindu
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
The inclusion of traditional medicine in WHOs internationally recognised health framework ensures that Indian health systems are officially documented and categorised

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Researchers have invented an entirely new field of microscopy -- nuclear spin microscopy. The team can visualize magnetic signals of nuclear magnetic resonance with a microscope. Quantum sensors convert the signals into light, enabling extremely high-resolution optical imaging.

HEALTHBEAT
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Public health, explained: Sign up to receive Healthbeats free Atlanta newsletter here. A community organizer and the Morehouse School of Medicine are launching a project to study the long-term physical and mental effects of a chemical plant fire outside Atlanta that polluted the air for over a month. About 17,000 Rockdale County residents were urged to evacuate their homes in September after the BioLab chemical plant caught fire , sending plumes of multicolored gas into the air , causing coughs,

Science Daily: Pharmacology News
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Discarded food scraps, stray branches, seashells and many other natural materials are key ingredients in a system that can pull drinkable water out of thin air developed by researchers.
News Medical Health Sciences
FEBRUARY 25, 2025
A new AI model can flag female patients who are at higher risk of heart disease based on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Let's personalize your content